What are we analysing?
We analyse addresses against more than 20 risk sources to find suspicious transactions and determine the risk factor. We categorise all sources into three categories.
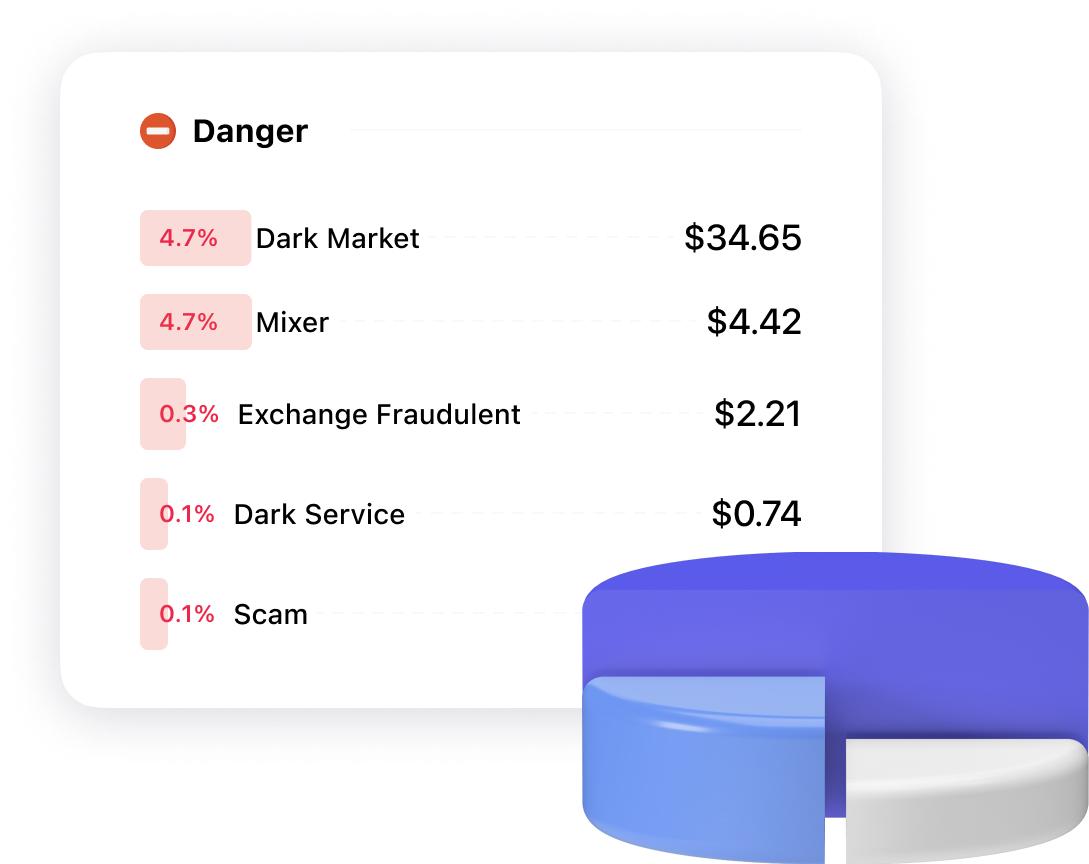
Danger
-
Child Exploitation
Entities involved in the exploitation of children. -
Dark Market
Coins associated with illegal activities. -
Dark Service
Coins related to child abuse, terrorist financing or drug trafficking. -
Enforcement action
A legal person is subject to judicial proceedings with the judicial authorities. -
Fraudulent Exchange
Exchanges involved in exit scams, unlawful behaviour, or from which funds have been confiscated by public authorities. -
Gambling
Coins associated with unlicensed online gambling. -
Illegal Service
Coins associated with illegal activities. -
Mixer
Coins passed through a mixer to make tracing difficult or impossible. Mixers are mainly used for money laundering. -
Ransom
Coins obtained by extortion or blackmail. -
Sanctions
Subjects subject to sanctions. -
Scam
Coins obtained by deception. -
Stolen Coins
Coins obtained by stealing other people's cryptocurrency. -
Terrorism Financing
Entities related to the financing of terrorism.
Suspicious sources
-
ATM
Coins obtained through a cryptocurrency ATM operator. -
Exchange | High Risk
An entity becomes high risk based on the following criteria:
No KYC: requires absolutely no customer information before authorising any level of deposit/withdrawal, or makes no attempt to verify this information.
Criminal ties: criminal charges against a legal entity for AML/CFT violations.
Impact: high exposure to risky services such as darknet markets, other high-risk exchanges or commingling is defined as a service whose direct exposure to high risk differs by one standard deviation from the average of all identified exchange organisations over a 12-month period.
Jurisdiction: based in a jurisdiction with weak AML/CFT measures.
Unlicensed: does not have any specific licence to trade cryptocurrency. -
Liquidity Pools
Smart contracts in which tokens are blockchained to provide liquidity. -
P2P Exchange | High Risk
The organisation does not hold any specific business licence to provide cryptocurrency exchange services where participants exchange directly with each other, without intermediaries.
This also includes organisations that are licensed but are located in listed jurisdictions, are on the FATF's list of non-cooperative companies or do not provide KYC for large value transactions, making them attractive for money laundering. -
Unnamed Service
The category refers to currently unidentified clusters that exhibit the behaviour expected from the service across a large number of addresses and transactions.
Trusted sources
-
Exchange
The organisation allows users to buy, sell and trade cryptocurrencies by holding trading licences that include the following aspects of services:
-Depository, brokerage or other related financial services that provide exchange services where participants interact with a central party.
And does not include:
-Licences for non-specific financial services and FATF-listed jurisdictions.
They represent the most important and most used category of entities in the cryptocurrency industry, on which the FATF's FATF list is based. -
ICO
An organisation that crowdfunds its project by selling its newly minted cryptocurrency to investors in exchange for fiat currency or more common cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin and ether.
There are many legitimate examples of such offerings, but there are also many cases where attackers raise funds through an ICO, then embezzle the money and disappear. -
Marketplace
Coins used to pay for legitimate activities. -
Merchant Services
An organisation that allows companies to accept payments from their customers, also known as payment gateways or payment processors.
It often facilitates conversion to local fiat currency and transfer of funds to the merchant's bank account. -
Miner
Coins mined by miners and not yet redirected. -
Other
Coins obtained through airdrops, token sales or other means. -
P2P Exchange
The organisation holds a business licence for cryptocurrency exchange services, where participants exchange directly with each other, without intermediaries.
This does not include licences for non-specific financial services and jurisdictions that are on the FATF's non-cooperative list. -
Payment Processor
Coins related to payment services -
Seized Assets
Crypto-assets seized by public authorities. -
Wallet
An online wallet is a service for storing and transacting cryptocurrency. Custodial wallets are one type of online wallet where the service stores the user's private keys, which can create potential risks of fraud or insufficient security, but in general reputable providers can provide better security than inexperienced users themselves.